FDA Using OoC Technology, French Senator to Request The Use of Liver-Chip For the Preclinical Stage, New Universal Animal Product-free Medium, and more
News on non-animal methods
JUNE 3 - 7, 2024NEWS, REPORTS & POSITION STATEMENTS
1. Latest British Toxicology Society (BTS) Public Statement
New Approach Methodologies (NAMs) collectively refer to technology-enabled strategies for obtaining information about the toxicity of chemicals without relying on traditional animal testing. These strategies have the potential to supplement, reduce, and eventually replace animal testing by uncovering the fundamental processes, often at the level of biomolecular interactions, that may make certain chemicals toxic to humans.
The science behind NAMs is not new. What is new about NAMs are the proposed regulatory applications of these strategies and technologies for protecting human health and the environment from chemical hazards. NAMs offer faster and less expensive means of gathering large volumes of data on the biological effects of chemicals. This information can help link specific chemical structures with their resulting biomolecular health outcomes. In time, this knowledge can be used to design safer chemicals rather than testing chemical products for safety after they have already been developed.
2. French senator’s request for the systematization of the use of liver-chip for the preclinical stage
Among adverse effects, drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is responsible for more than 20% of drug withdrawals from the market and 13% of clinical trial failures. In a written question submitted at the end of May 2024 to the French Minister of Labor, Health and Solidarity, Senator Arnaud Bazin asked if there are any plans to institute systematic use of liver-chip to obtain marketing authorization for medicines and, if so, within what time frame.
The question echoes the landmark study published by Emulate, and the current development and advances of the OoC technology around the globe and already used in the pharmaceutical industry in order to better identify and assess potential adverse effects of drugs in the preclinical stage.
Read the question addressed to the French Minister (FR)
INTERVIEWS, NOMINATIONS & AWARDS
3. Owkin won the Prix Galien Award
Also awarded by Le Point in its 2024 list of inventors that could play a key role in the Medtech sector, Owkin announced having won the Prix Galien Award in the category of Best Medical Technology for its product, MSIntuit CRC. MSIntuit CRC. is the first and only CE-marked AI diagnostic for MSI (DNA MicroSatellite Instability) testing in colorectal cancer from digital H&E (hematoxylin and eosin staining) slides
Co-founded by Thomas Clozel, Owkin makes generative AI that connects all stages of biology by using data from American and European hospitals to transform it into knowledge, aiming at revolutionizing and augmenting pharmaceutical research using artificial intelligence (IA).
4. French Tech : Netri winner of the Nextinnov Prize
For the 7th edition of the Nextinnov Prize, organized by Banque Populaire and Maddyness, Netri won the Sovtech prize (National Technological Sovereignty). Netri is an industrial startup which offers health industries the generation of mini human organs-chips which, coupled with AI, makes it possible to predict the clinical effect of a drug candidate.
This year, the competition awarded a Startup Grand Prize, a Sovtech Prize, and an SME “innovative services and products” prize. In addition to the first three prizes, two mentions were awarded, one for Healthtech companies (Healthtech mention) and the other for those with strong potential for international development (internationalization mention). Finally, during the awards ceremony, a live vote allowed the public to choose their favorite (public vote).
Learn more about the Nextinnov Prize (FR)
5. ENACT : winner of the call for expressions of interest “AI Cluster”
ENACT (European Center for Artificial Intelligence Through Innovation) supported by the University of Lorraine is the winner of the call for expressions of interest “AI Cluster : world-class research and training centers in artificial intelligence” (ANR by France 2030)
The Cluster aims at equipping scientists and professionals with a solid foundation in AI science, a mastery of advanced tools and concepts, as well as the ability to implement them in innovative ways. Emphasizing an interdisciplinary approach and group projects at different academic levels, the idea is to encourage the practical application of knowledge and collaboration between different disciplines to solve complex problems. ENACT will carry out research and innovation activities around three main axes : Natural language processing and large multimodal language models ; Engineering and scientific discovery ; and Digital health.
TOOLS, PLATFORMS, CALLS
6. ESTIV 2024 : the ILSI Europe Survey on human tissue applications
ILSI Europe contributes to ESTIV 2024 in engaging ESTIV members and followers in a questionnaire and short survey on human tissue applications.
These resources, curated by the Expert Group on Human Tissue appointed by ILSI Europe’s Alternatives to Animal Testing Task Force, aim to foster engagement and ignite fresh perspectives. The participation in both endeavours will enhance the discourse on this subject and drive us towards innovative solutions.
The aim of the survey is to compile valuable insights into the diverse types of human cells or tissue-based models used by end-users for toxicological studies, drug development, disease modeling, and other related applications.
The questionnaire explores the viability of using human tissues as a replacement for animal testing.
To take part in the short survey
To engage in the questionnaire
7. Comment of the COLAAB’s Author guide for addressing animal methods bias
Non-animal biomedical research methods have advanced rapidly over the last decade making them the first-choice model for many researchers due to improved translatability and avoidance of ethical concerns. Yet confidence in novel non-animal methods is still being established and they remain a small portion of nonclinical biomedical research, which can lead peer reviewers to evaluate animal-free studies or grant proposals in a biased manner.
An international team of researchers and advocates called the Coalition to Illuminate and Address Animal Methods Bias (COLAAB), recently awarded the Lush Prize, aims to provide concrete evidence of the existence and consequences of this bias and to develop and implement solutions towards overcoming it. In their latest article, the authors provided comments on the COLAAB’s Author Guide for Addressing Animal Methods Bias in Publishing, and described it along with broader implications and future directions.
INDUSTRY, BIOTECH & PARTNERSHIPS
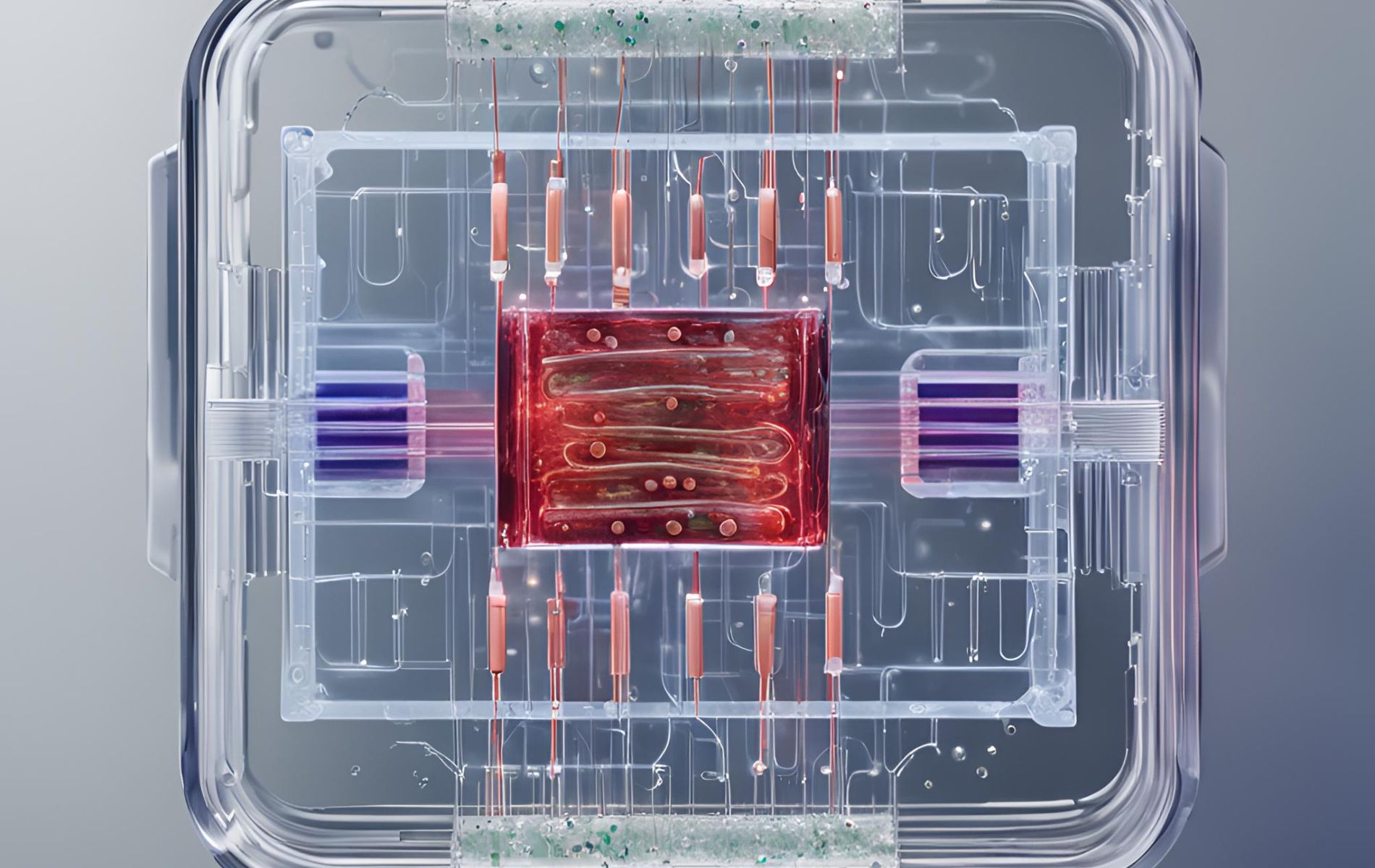
8. How FDA is using OoC technology to Improve drug evaluation research
Following the article by Emulate on how Moderna is using Organ-Chips to improve their LNP research, the FDA shares, through an educational and informative video series on YouTube (YT), its achievements and commitment to public health, drug development and towards better evaluation methods to predict drug effects in the clinic. The short videos are suitable for a wide range of public, whether scientist, healthcare professional, student, or simply curious about the world of regulatory science. In two recent videos posted on YT, the FDA shows how its researchers are using OoC technology to Improve drug evaluation research.
Watch the short video on the Division of Applied Regulatory Science
Watch the FDA video on Cardiac OoC
SCIENTIFIC DISCOVERIES & PROTOCOLS
9. A multicellular vessel-on-a-chip model reveals roles for platelets in inflammation
The immune system identifies and destroys invading pathogens. However, chronic inflammation and excessive tissue damage can occur if inflammation is not resolved or if the immune system misidentifies a threat. Until recently, research into inflammation heavily relied upon in vivo animal models or simple in vitro models. But there are critical differences between the innate immune system of mice and humans that limit the translational impact of these models.
In a new study, Rebecca B. Riddle et al. developed multicellular models of inflammation and inflammatory hemostasis that incorporate platelets and red blood cells. They demonstrated how the inclusion of platelets alters vascular integrity in organ-on-a-chip models, creating a more complete representation of how vascular integrity is regulated in vivo. Their model successfully proved the feasibility of investigating complex cellular interactions in in vitro models.
10. Filling key women’s health gap with the human Cervix-on-a-Chip
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) affects more than 25% of reproductive-aged women. It is caused by pathogenic bacteria that push the healthy microbiomes in the female vagina and cervix into a state of imbalance. Thus far, the only treatments for BV are antibiotics, which often fail to kill the invading bacteria in the infected vagina and cervix.
Wyss researchers have developed a human Cervix-on-a-Chip that models the complex cervix tissue in vitro, and overcomes major limitations of existing animal and in vitro models to enable the study of BV and development of drugs.
11. New universal cell culture medium with human-derived protein
Easy to use, do-it-yourself and beneficial for 2D and 3D culturing of normal and cancer cells, a new universal cell culture medium with human-derived proteins – known as Oredsson Universal Replacement (OUR) – to replace fetal bovine serum has been developed by Stina Oredsson, Atena Malakpour Permlid, Tilo Weber, Jeffrey Bajramovic.
OUR medium is successfully used with human normal and cancer-associated fibroblasts, human keratinocytes, several human breast and pancreatic cancer cell lines, human colon cancer CaCo‑2 cells as well as several other normal and cancer cells. Researchers presented their work at the 3R Länd conference, a poster presenting the composition of OUR defined medium, and why this medium is providing a leap towards a universal animal product-free cell culture medium.
UPCOMING WEBINARS, WORKSHOPS, SYMPOSIA
MPS World Summit 2024 : June 10 – June 14, 2024, Seattle (US)


